Are Sinus Infections Contagious: Discover In 8 Crucial Steps

If you’re curious about whether sinus infections are contagious, come, let me unfold all the secrets for you. Here, I’ve gathered the information you’re seeking – from the types and causes to symptoms, treatment, and prevention of sinus infections. So, let’s dive in to know are sinus infections contagious?
Table of Contents
Are Sinus Infections Contagious?
Sinus infections themselves are generally not contagious. However, the underlying causes of sinusitis, such as viral or bacterial infections, can be contagious. For example, the viruses that cause the common cold or the flu can spread from person to person through respiratory droplets.
If someone has a sinus infection caused by a contagious agent, they can potentially transmit that agent to others through coughing, sneezing, or close contact. It’s essential to practice good respiratory hygiene, such as covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, to prevent the spread of infectious particles.
While sinus infections themselves are not directly contagious, it’s crucial to be mindful of the potential for spreading the underlying infections that can lead to sinusitis. If you have symptoms of a respiratory infection, it’s advisable to take precautions to prevent the transmission of viruses or bacteria to others.
What Is A Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)?
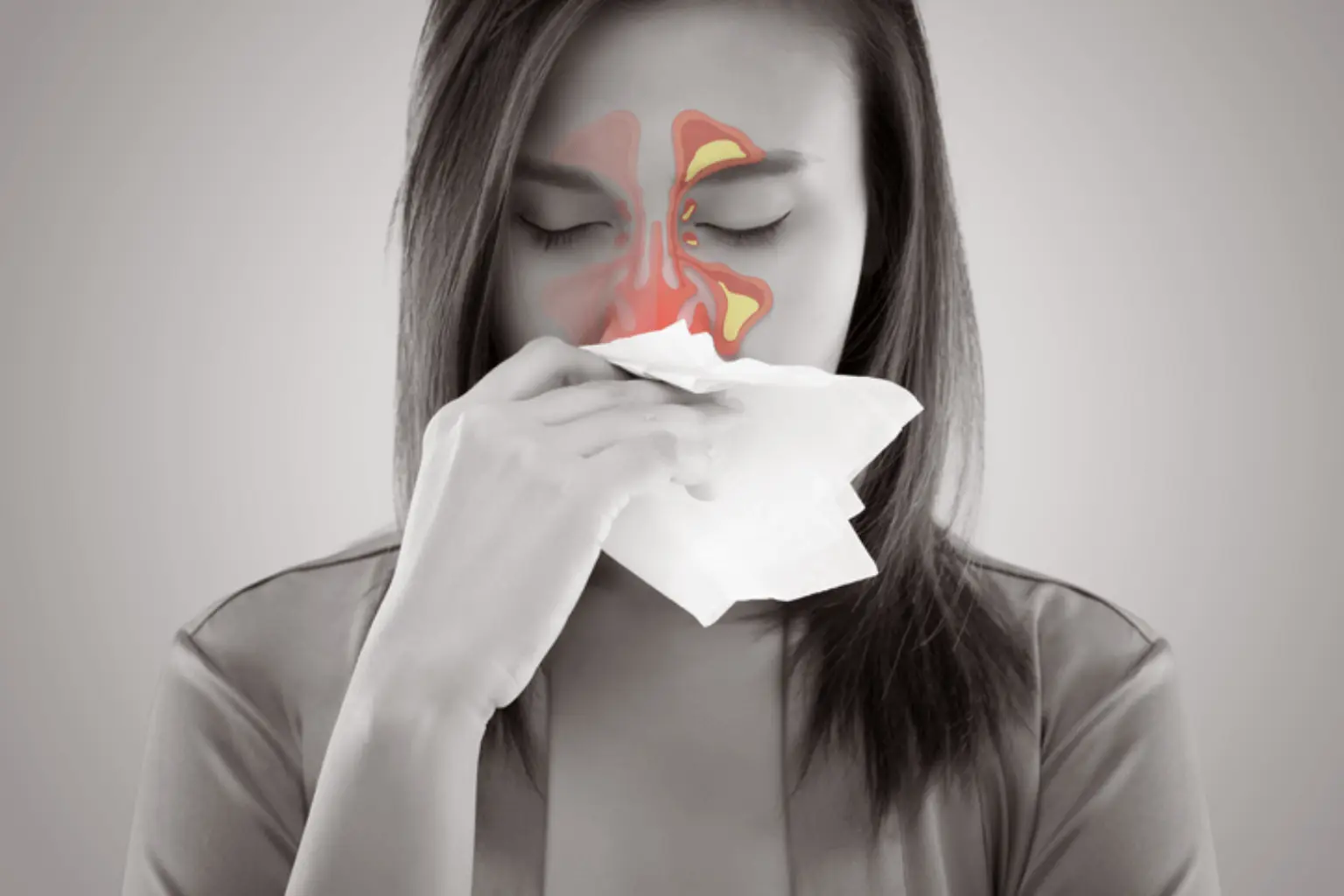
Sinusitis, commonly known as a sinus infection, is the inflammation or swelling of the tissue lining the sinuses. The sinuses are hollow cavities within the bones surrounding the nose, and they produce mucus that helps to moisten and filter the air we breathe. When the sinuses become inflamed, they can trap mucus and cause pressure, leading to discomfort and various symptoms.
Types Of Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
Sinusitis can be categorized into several types based on its duration and cause:
- Acute Sinusitis: This type typically lasts for a short period, usually less than four weeks. It is often associated with a cold or respiratory infection and can cause symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain or pressure, headaches, and discharge from the nose.
- Subacute Sinusitis: This type lasts longer than acute sinusitis but less than 12 weeks. Symptoms may be similar to acute sinusitis but persist for a more extended period.
- Chronic Sinusitis: Chronic sinusitis lasts for 12 weeks or longer and may be caused by an infection or other factors, such as nasal polyps, deviated nasal septum, or allergies. Symptoms may include congestion, discolored nasal discharge, and facial pain or pressure.
- Recurrent Sinusitis: This type involves multiple acute sinusitis episodes within a year.
Based On The Underlying Cause:
- Viral Sinusitis:
- Cause: Triggered by viruses, commonly associated with upper respiratory tract infections like the common cold or influenza.
- Duration: Can be acute or subacute.
- Bacterial Sinusitis:
- Cause: Caused by bacterial infections that may follow a viral infection or occur independently.
- Duration: Can be acute, subacute, or chronic.
- Allergic Sinusitis (Allergic Rhinitis):
- Cause: Results from an allergic reaction to airborne allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold.
- Symptoms: Often characterized by sneezing, itching, and watery eyes in addition to sinusitis symptoms.
- Fungal Sinusitis:
- Cause: Caused by fungal infections, typically in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Types: Includes allergic fungal sinusitis, chronic indolent sinusitis, and acute fulminant sinusitis.
What Are The Causes Of A Sinus Infection?
Sinus infections, or sinusitis, can be caused by various factors. The condition typically arises when the sinuses, which are hollow cavities in the skull, become inflamed or swollen. The primary causes of sinus infections include:
- Viral Infections:
- Common Cold and Influenza: Viral infections, such as those causing the common cold or influenza, are frequent culprits for sinusitis. These infections can lead to inflammation and swelling of the sinus linings.
- Bacterial Infections:
- Secondary Infections: Bacterial sinusitis can occur as a secondary infection following a viral upper respiratory infection. The initial viral infection weakens the immune system and creates an environment conducive to bacterial growth.
- Allergies:
- Allergic Rhinitis: Allergies to airborne particles, such as pollen, dust, mold, pet dander, or certain foods, can trigger allergic rhinitis. This allergic reaction can cause inflammation in the nasal passages and sinuses, leading to sinusitis.
- Nasal Polyps:
- Non-Cancerous Growths: Nasal polyps are small, benign growths that can develop in the nasal passages or sinuses. They may obstruct the normal flow of mucus, leading to sinusitis.
- Deviated Nasal Septum:
- Crooked or Off-Center Septum: A deviated nasal septum, which is a displacement of the wall between the nostrils, can obstruct the nasal passages. This obstruction can contribute to the development of sinusitis.
- Respiratory Tract Infections:
- Other Respiratory Infections: Infections in the respiratory tract, such as bronchitis or pneumonia, can sometimes spread to the sinuses, leading to sinusitis.
- Immune System Deficiencies:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, either due to certain medical conditions or medications, may be more susceptible to sinus infections.
- Cystic Fibrosis:
- Genetic Disorder: Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that can affect the respiratory system, leading to the production of thick and sticky mucus. This can block the sinuses and contribute to sinusitis.
- Dental Infections:
- Tooth Infections: Infections in the teeth, particularly the upper molars, can sometimes spread to the adjacent sinuses, causing sinusitis.
- Swimming and Diving:
- Water in Sinuses: Water-related activities, such as swimming or diving, can introduce bacteria or fungi into the sinuses, potentially leading to sinusitis. This is known as “swimmer’s sinusitis.”
What Are The Symptoms Of A Sinus Infection?
Sinus infections, or sinusitis, can manifest with a variety of symptoms. The specific symptoms can vary depending on the type of sinusitis (acute, subacute, chronic) and its underlying cause. Common symptoms of sinus infection include:
- Nasal Congestion:
- Difficulty breathing through the nose due to blockage or swelling of the nasal passages.
- Facial Pain or Pressure:
- Discomfort or pressure in the face, particularly around the eyes, forehead, or cheeks.
- Headache:
- Sinus headaches are often characterized by pain and pressure in the forehead or around the eyes. The pain may worsen with movement or when bending forward.
- Discolored Nasal Discharge:
- Thick, discolored mucus drainage from the nose, which may be yellow, green, or cloudy.
- Loss of Smell:
- Impaired or complete loss of the sense of smell (anosmia) due to inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Cough:
- A persistent cough, which may be worse at night, especially if the sinus drainage irritates the throat.
- Sore Throat:
- Irritation or discomfort in the throat, often associated with postnasal drip.
- Fatigue:
- Feeling tired or lethargic, which can be a result of the body’s response to infection.
- Bad Breath:
- Foul-smelling breath may occur due to the presence of infection and mucus in the sinuses.
- Ear Pressure or Fullness:
- Sensation of fullness or pressure in the ears due to congestion in the nasal passages affecting the Eustachian tubes.
- Dental Pain:
- Pain or discomfort in the upper teeth, especially in the molars, which may be related to sinus pressure.
- Fever:
- In some cases, sinusitis can cause a low-grade fever, particularly in bacterial sinus infections.
How Long Does A Sinus Infection Last?
The duration of a sinus infection, or sinusitis, can vary depending on the type and underlying cause of the condition. Here are the general timelines for different types of sinusitis:
- Acute Sinusitis:
- Duration: Acute sinusitis typically lasts for a short period, usually less than four weeks.
- Common Cause: Often triggered by a viral upper respiratory infection (common cold) or less commonly by a bacterial infection.
- Subacute Sinusitis:
- Duration: Subacute sinusitis lasts longer than acute sinusitis but less than 12 weeks.
- Cause: Similar to acute sinusitis, it may be associated with viral or bacterial infections.
- Chronic Sinusitis:
- Duration: Chronic sinusitis persists for 12 weeks or longer.
- Cause: Can result from various factors, including persistent viral or bacterial infections, allergies, nasal polyps, a deviated nasal septum, or other underlying health conditions.
How Can I Treat A Sinus Infection At Home?
While it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, there are several home remedies and self-care measures that may help alleviate symptoms of a sinus infection. Here are some at-home treatments you can consider:
- Nasal Irrigation:
- Use a saline solution to irrigate your nasal passages. This can help clear mucus, reduce inflammation, and promote drainage. You can use a saline nasal spray or a neti pot for irrigation.
- Warm Compresses:
- Apply warm compresses to your face to help soothe sinus pain and reduce facial pressure. Use a warm, damp cloth and place it over your forehead, nose, and cheeks.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, herbal teas, and clear broths, to stay hydrated. Adequate hydration can help thin mucus and promote drainage.
- Rest:
- Get plenty of rest to allow your body to recover. Adequate rest supports your immune system and helps your body fight the infection.
- Steam Inhalation:
- Inhale steam to help relieve congestion. You can do this by sitting in a steamy bathroom or using a humidifier. Adding a few drops of eucalyptus oil to the water may enhance the decongestant effect.
- Over-the-Counter Medications:
- Non-prescription decongestants and pain relievers, such as pseudoephedrine or ibuprofen, may help alleviate symptoms. However, use them according to package instructions and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or existing medical conditions.
- Elevate Your Head:
- Use an extra pillow to elevate your head while sleeping. This can help promote sinus drainage and reduce nighttime congestion.
- Avoid Irritants:
- Avoid exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke and strong odors, as they can aggravate nasal passages and worsen symptoms.
- Hot or Cold Packs:
- Apply hot or cold packs over the affected areas to help reduce pain and inflammation. A cold pack may be more suitable for relieving sinus headaches, while a warm pack can soothe facial pressure.
- Stay Warm and Moist:
- Keep your living spaces warm and humidified, especially during dry weather. Moist air can prevent nasal passages from drying out.
- Nasal Strips:
- Nasal strips can help open nasal passages and improve airflow, making it easier to breathe.
- Avoid Overuse of Decongestant Nasal Sprays:
- While decongestant nasal sprays can provide short-term relief, their overuse can lead to rebound congestion. Use them according to the package instructions and for the shortest duration possible.
What Are The Best Medications For A Sinus Infection?
If you need an antibiotic, which one your provider prescribes depends on your specific situation. Some options include:
- Augmentin (amoxicillin/clavulanate).
- Amoxicillin.
- Doxycycline.
- Levofloxacin.
- Cefixime.
- Cefpodoxime.
- Clindamycin.
Are Complementary And Alternative Therapies Useful For Treating Sinusitis?
Complementary therapies such as nasal irrigation and acupuncture may provide symptom relief for sinusitis, but they should be used alongside conventional medical treatments. Consultation with healthcare professionals is crucial for a comprehensive and safe approach.
Do I Need Antibiotics For Every Sinus Infection?
Not every sinus infection requires antibiotics. Sinusitis can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or other factors. Viral sinusitis is more common and doesn’t respond to antibiotics; it typically resolves on its own. Antibiotics are generally prescribed for bacterial sinus infections, and a healthcare professional can determine the appropriate treatment based on the specific cause and severity of your symptoms.
How Can I Prevent Sinus Infections?
While it may not be possible to prevent all sinus infections, certain lifestyle habits and preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing sinusitis. Here are some strategies to consider for preventing sinus infections:
- Practice Good Hand Hygiene:
- Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially after being in public places or around individuals with respiratory infections.
- Avoid Touching Your Face:
- Avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth, to minimize the risk of introducing viruses or bacteria into the respiratory system.
- Maintain a Healthy Immune System:
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management to support a strong immune system.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink plenty of water to keep the mucous membranes in the respiratory tract hydrated, which can help prevent the trapping of mucus in the sinuses.
- Use Humidifiers:
- Use humidifiers in your living spaces, especially during the dry winter months, to maintain optimal humidity levels. Moist air can help prevent nasal passages from drying out and becoming more susceptible to infections.
- Avoid Environmental Irritants:
- Minimize exposure to airborne irritants, such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, strong odors, and chemicals, which can irritate the nasal passages and contribute to sinusitis.
- Manage Allergies:
- Identify and manage allergy triggers, such as pollen, dust, mold, and pet dander, to reduce the risk of allergic rhinitis leading to sinus infections.
- Practice Nasal Irrigation:
- Use saline nasal sprays or perform nasal irrigation with a neti pot to help clear mucus and reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Avoid Overuse of Decongestant Nasal Sprays:
- Limit the use of over-the-counter decongestant nasal sprays, as overuse can lead to rebound congestion and worsen symptoms.
- Seek Prompt Treatment for Respiratory Infections:
- If you develop symptoms of a respiratory infection, such as a cold or flu, seek prompt medical attention. Treating viral infections early may help prevent secondary bacterial infections that can lead to sinusitis.
- Address Dental Issues:
- Address dental problems promptly, as untreated dental infections, especially in the upper teeth, can spread to the adjacent sinuses.
- Practice Sinus-Friendly Activities:
- If you engage in activities like swimming or diving, take precautions to prevent waterborne infections, such as wearing a nose clip to avoid introducing pathogens into the sinuses.
When Should You See A Doctor?
Call or see the doctor immediately if you have:
- a fever above 102°F (38.8°C)
- problems seeing or double vision
- swelling and redness around the eyes
- a swollen forehead
- a stiff neck
- confusion
- intense pain and headaches that don’t go away
- sinus symptoms that last more than 12 weeks
You should also see your doctor if you have multiple sinus infections in 12 months or if OTC medications don’t improve your symptoms.
In some cases, sinus infections can lead to other complications. Contact a doctor immediately if you have:
- other infections, including osteomyelitis (bone infection) or cellulitis (skin infection)
- loss of smell that is permanent or temporary
- meningitis
Conclusion
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the causes, symptoms, and treatments for sinus infections empowers individuals to navigate and manage this common condition effectively. While viral sinus infections can be contagious, bacterial infections typically are not. Prompt medical attention, proper diagnosis, and a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments can help individuals manage and prevent sinus infections. By staying informed and adopting preventive measures, individuals can take control of their sinus health, ensuring a better quality of life.
FAQ’s
Read more How to Cure Plantar Fasciitis in One Week: 8 Symptoms